Carnosine first appeared in the mainstream health community around a decade ago in the form of supplements, eye drops, and skin creams. Companies touted carnosine as an “elixir of youth.” Fast forward ten years and there is still insufficient evidence to back up the alleged benefits of carnosine supplementation. Read on to discover the unbiased science behind this compound.
What is Carnosine?
Overview
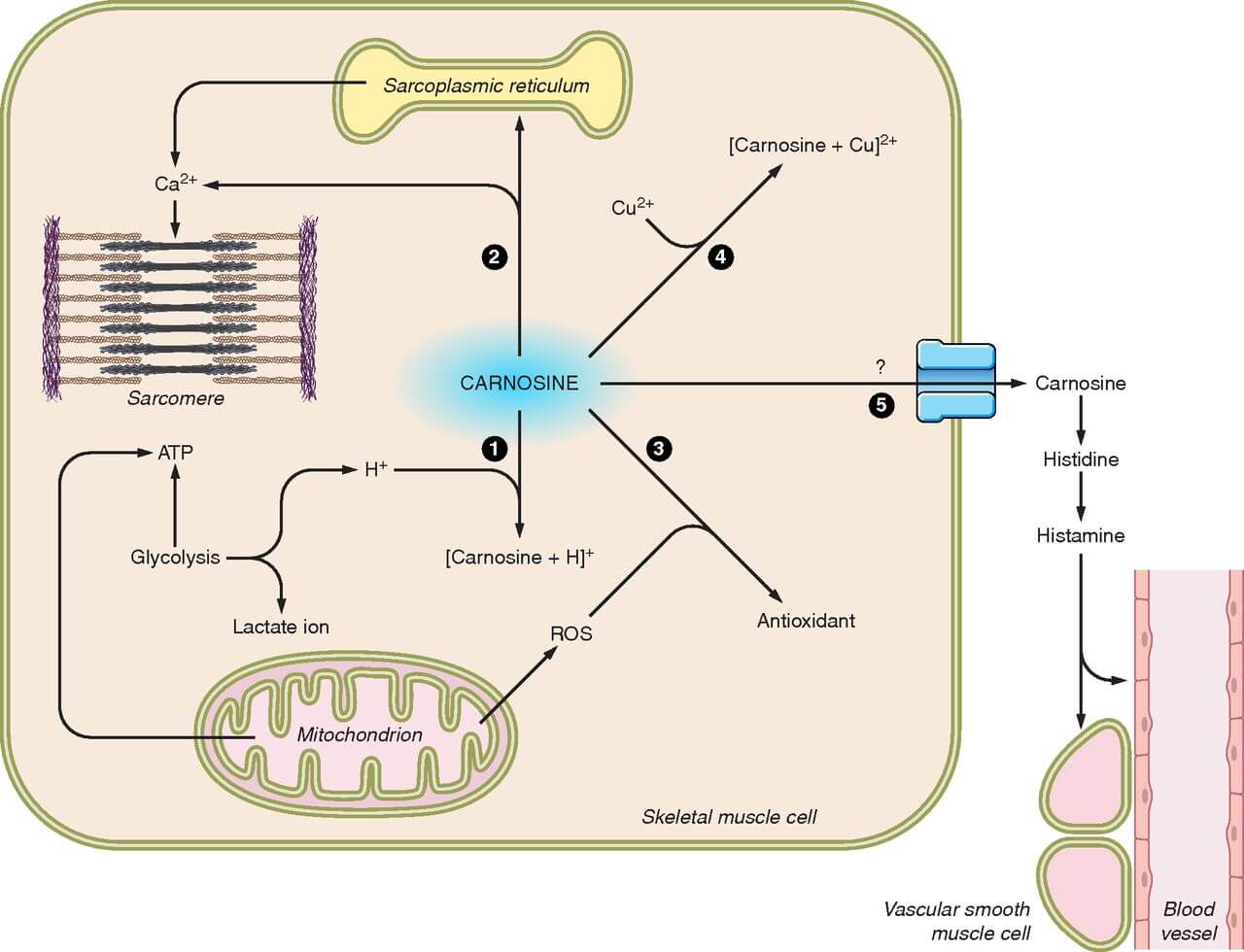
Carnosine is a peptide made by combining two amino acids: beta-alanine, and histidine [1].
Scientists discovered that it is present in the brain, kidney and skeletal muscle of fish, birds, and mammals. Some hypothesize that carnosine has the capability to affect many different tissue types [2, 3].
Ongoing research is investigating its effects on preventing cellular damage from free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species (like hydroxyl radicals and superoxide) and reactive nitrogen species. Nonetheless, clinical data are lacking to back up these effects [3].
Limited human studies have researched potential associations between various disease states and carnosine levels. However, proper clinical trials on the effectiveness and safety of carnosine supplementation are lacking [4, 5, 6].
Additionally, carnosine supplements have not been approved by the FDA for medical use. Supplements generally lack solid clinical research. Regulations set manufacturing standards for them but don’t guarantee that they’re safe or effective. Speak with your doctor before supplementing.
Snapshot
Proponents
- Alleged anti-aging capabilities
- May support healthy blood sugar levels
- May be good for gut health, cognition & memory
- Brain-protective potential being researched
Skeptics
- Proper clinical trials lacking
- Drug interactions possible
- Long-term safety unknown
- May interfere with blood clotting
Purported Health Benefits of Carnosine
Insufficient Evidence For:
The following purported benefits are only supported by limited, low-quality clinical studies. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of carnosine for any of the below listed uses.
Remember to speak with a doctor before taking carnosine supplements. Carnosine should never be used as a replacement for approved medical therapies.
1) Memory
Insufficient evidence backs up the use of l-carnosine for memory problems, though early trials show some promise. Large-scale clinical trials are needed.
One study found that after 3 months of Carnosine supplementation at 500mg/day, patients performed better on verbal episodic memory tests [7].
Similarly, another study demonstrated improved verbal episodic memory in elderly people when they were given a combination of Anserine & Carnosine [8].
Scientists are also investigating the combination of carnosine with other compounds – such as polyphenols from blueberry and green tea and other amino acids – and its effects on neuronal health and neurogenesis in cells [9].
2) Autism
There is insufficient evidence to support the use of l-carnosine for autism.
In one small clinical trial of 31 children with autism, L-carnosine (800 mg/day) improved autism severity and symptoms (such as socialization, communication, and vocabulary) after 8 weeks. However, we can’t draw any conclusions from this single study that lacked an active control group [10].
3) Dry Skin & Wound Healing
Insufficient evidence supports the use of l-carnosine for dry skin, though small-scale human studies show promise.
In one clinical trial of 50 people with diabetes and severely dry foot skin, a cream containing urea 5%, arginine 0.5%, and carnosine 0.01% (Ureadin Podos Db cream) improved skin hydration and reduces skin dryness. When compared with a control emollient cream, patients who applied the carnosine cream twice daily for 8 months had reduced dryness by 91% (compared with 23% with the control cream) [11].
On the other hand, no clinical data back up the use of l-carnosine for wound healing. Only animal data are available, and we can’t draw any conclusions until human studies are carried out.
In one rodent study, carnosine (100mg/kg internally and applied topically) improved wound healing. Scientists suspect it increased the expression of beneficial growth factors and cytokines [12].
Researchers are also investigating the effects of carnosine increased on human skin and blood vessel cells in the presence of high glucose [12].
4) Heart Health
Insufficient evidence supports the use of l-carnosine for heart health or in people with heart failure.
In one clinical study of patients with heart failure, carnosine as an add-on to standard treatment improved some markers of heart function (such as oxygen uptake), which increased the patients’ walking distance [13].
Scientists hypothesized that carnosine may improve heart function by regulating cellular calcium levels, based on animal findings. Others are investigating whether it provides protection against the hardening of arteries, but data are still lacking [14, 15+, 16].
5) Obesity and Pre-Diabetics
Insufficient evidence supports the use of carnosine in people with obesity and/or prediabetes or diabetes.
Some scientists suggest that people who are diabetic or pre-diabetic have low concentrations (63% below normal) of carnosine in their muscle and brain cells. Large-scale studies have not verified their findings [4].
In one small study, obese individuals who were given carnosine had a decrease in their blood sugar levels. These findings have not been replicated [17].
Carnosine researchers hypothesized that this compound might strengthen the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves that communicate with the adrenal glands, liver, kidney, pancreas, stomach, and white and brown fat tissues. These tissues all contribute to blood sugar and blood pressure control, appetite, and fat burning. Their theories, however, remain unproven [18].
Other research groups are exploring the effects of carnosine on the complications of diabetes, (such as neuropathic pain, organ failure, hearing loss, osteoporosis, eye problems, and heart damage) in animals and cells [19, 20, 21, 22, 3].
In cells, carnosine is being studied for preventing the formation of glycated low-density lipoprotein, which can stimulate the formation of foam cells that are linked with circulatory disorders commonly seen in diabetics [23].
6) Eye Health & Glaucoma
In a small trial, a combination supplement called Gangliolife taken twice daily for one year as an add-on to standard therapy reduced intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma [24].
One tablet of the supplement contains coleus extract 150 mg (standardized to 10% forskolin), homotaurine 100 mg, L-carnosine 50 mg, vitamin B1 1.1 mg, vitamin B2 1.4 mg, vitamin B6 1.4 mg, folic acid 0.2 mg, and magnesium 150 mg. The contribution of carnosine to the observed effect is unknown [24].
Russian scientists suggest that carnosine prevents cataracts via a combination of its antioxidant and anti-glycating properties, but large-scale clinical data are lacking [25].
The use of carnosine-containing eye-drops for 2 to 6 months reduced vision deficiencies (measured by lens opacity & visual acuity) that are usually a side effect of cataracts [26, 27].
Possibly Ineffective For:
7) Physical Performance
There is insufficient evidence to rate the effects of carnosine on physical performance. The existing data are mixed.
In one study of muscle-fatigued healthy men, a single dose of carnosine 2 grams plus beta-alanine 2 grams 4 hours prior to testing increased some measures of physical performance (maximal muscle contractions during knee extensions and jump height). However, it also increased muscle pain after 24 hours [28].
In another study, a single oral dose of a chicken breast extract (40 grams containing 1.5 grams of carnosine and anserine) did not affect power during intense rower sprints in healthy men compared to placebo [29].
Limited studies have reported that β-alanine (precursor of Carnosine) supplementation can increase high-intensity exercise performance, lean muscle gains, VO2 max, and the speed of training adaptations. Researchers suspect the mechanism may at least partly be attributable to carnosine’s ability to increase muscle buffering capacity [30].
8) Schizophrenia
There is insufficient evidence to suggest that carnosine improves cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Its potential interactions with antipsychotic drugs are also unknown.
In one study, carnosine did not improve symptoms of depression or schizophrenia or quality of life in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder on stable doses of antipsychotics. It was dosed up to 2000 mg over 4 weeks and continued for 8 more weeks [3].
Carnosine may improve cognitive function in people with schizophrenia, but it’s unclear if its effects are meaningful. More research is needed [3].
Lacking Evidence For:
No clinical evidence supports the use of carnosine for any of the conditions listed in this section.
Below is a summary of the existing animal and cell-based research, which should guide further investigational efforts. However, the studies listed below should not be interpreted as supportive of any health benefit.
Anti-Aging & Longevity Potential
Some scientists think carnosine might have anti-aging properties, but no valid data backs up their hypotheses. They suggest that carnosine levels decline with age in rats [31].
Researchers in Australia are investigating the effects of carnosine in cells. They say carnosine might “reinvigorate cells” as they approach senescence (the stage just before they die when the cell is not functioning), making them look and behave younger than untreated cells. However, we can’t draw any conclusions from studies in cells [4, 32].
In one study, 44% of mice given carnosine had young, healthy-looking fur into old age, compared to just 5% of the untreated mice. Similarly, 9% of the untreated mice behaved youthfully in old age, whereas 58% of the mice treated with Carnosine showed youthful vigor. These findings have never been replicated, however [33, 34].
Another research group considers protein glycation — the reaction of protein and sugars in the bloodstream that damages the proteins and is a potential factor in aging — a possible target of carnosine. It’s being researched for the following in cells:
- Bonding with the carbonyl/aldehyde groups that would otherwise bind with and damage proteins [35].
- Limiting the formation of oxidized sugars, commonly known as Advanced Glycosylation End-products (AGEs) by acting as an antioxidant. From a theoretical anti-aging perspective, the fewer AGEs created in your body the better [36, 37].
- Reducing lipid, DNA, and protein damage by chelating metals [2].
- Sparing proteins such as Hsc-70 from glycation [38].
None of these mechanisms have been confirmed.
According to limited research, vegetarians have higher levels of these AGEs than omnivores. Some scientists think this may be because of the absence of Carnosine in vegetarian diets – although they point out how high fructose consumption could also play a role [39].
When placed in the connective tissue of rats, carnosine promoted the production of vimentin. It has been suggested that vimentin plays a role in the elimination of oxidized proteins (via oxidized protein hydrolase) that contribute to aging [3, 40].
And, like many experimental compounds, carnosine increased the average lifespan of fruit flies. However, it only had an effect on the males, but triggered no change in the average lifespan of females [41].
Mitochondrial Health
Italian researchers suggested that old mice given carnosine had less age-related mitochondrial dysfunction [42].
Gut Health
Scientists are exploring the effects of zinc carnosine on hair-like structures, called villi, that line the gut. They are also studying whether it can reduce gut inflammation and protect the gut from indomethacin, an anti-inflammatory drug that can damage the gut lining [43].
Another research team is looking at its effects on pro‐inflammatory cytokines in gut cells that are exposed to Helicobacter pylori [43].
Neurodegeneration
Malondialdehyde (MDA) is a toxic end-product of lipid peroxidation. A study on rats suggested that carnosine protects against MDA-induced toxicity in animals and inhibits protein modification caused by MDA (deleterious formation of cross-links and carbonyl groups) [44].
Taking common anesthetics often results in an increase in serotonin-derived melanoid (SDM). Carnosine protected against the neurotoxic effects of SDM in animals (45, 46, 47, 48).
It also improved neurological function after a stroke-like event and protected against cognitive decline caused by a high-fat diet. It also had antidepressant activity in rats, but human data are completely lacking (45, 46, 47, 48).
Carnosine-specific transporters are found in parts of the blood-brain barrier [49].
Scientists are investigating if carnosine can protect the mitochondria of cultured brain cells (astroglia) against nitric oxide-induced damage [50].
Because carnosine binds to zinc, some researchers believe it plays some role in controlling the availability of zinc ions in neuronal tissue, especially the olfactory lobe where both Carnosine and zinc are found in high amounts [51].
Immune Response & Inflammation
In rats, Carnosine decreases IL-1a and normalizes levels of gamma-glutamyltransferase [52].
Scientists are exploring whether carnosine reduces inflammation by lowering TNF-a as well as nitric oxide synthesis in brain tissue [53].
Cancer Research
L-carnosine has not been shown to prevent or treat cancer. Most of the studies are limited to cells, which makes their findings impossible to interpret.
Remember that many substances have anti-cancer effects in cells, including downright toxic chemicals like bleach. This doesn’t mean that they have any medical value. On the contrary, most substances (natural or synthetic) that are researched in cancer cells fail to pass further animal studies or clinical trials due to a lack of safety or efficacy.
Researchers are investigating the effects of carnosine on the following pathways in cells (or animals):
- DNA damage that can, in theory, transform healthy cells into cancerous cells [54, 55, 56].
- ATP levels in cancer cells [3].
- Cancer development in vitamin E-deficient rats [57].
- MMP-9 gene expression in liver cancer cells [58].
- AGEs in cells, implicated in cancer [3].
- Caspase 3 in neck cancer cells [59].
- The expression of Hsp27r combined with a protein shell (capsid) of an oncolytic adenovirus on lung cancer cells [60].
- Mitochondrial oxidative stress in ovarian cancer cells [61].
- In the presence of pyruvate or other metabolic intermediates (oxaloacetate and a-ketoglutarate), which may counter its effects in cells [62].
Human data are completely lacking and even animal studies are sparse. Therefore, the effects of carnitine on cancer are unknown.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Limited data linked low blood levels of Carnosine with Alzheimer’s [6].
It’s being researched for counteracting the build-up of aldehydes and amyloid plaques, which are widely considered to be the primary causes of Alzheimer’s [63].
The aggregation of beta-amyloid into fibrillar structures contributed to Alzheimer’s disease. Carnosine is hypothesized to impede the formation of fibrillar structures by altering the hydrogen bond network involved in fibrillogenesis [64].
Researchers are studying whether carnosine might mitigate the effects of beta-amyloid in cultured rat brain cells [65].
They have proposed that Carnosine may protect the brain via the regulation of glutamate release, but this theory remains unproven [66].
Limited findings suggest that carbonic anhydrase is lower in Alzheimer’s patient brains. Carnosine is hypothesized to act as a Carbonic anhydrase activator [5].
One controversial theory suggested that an imbalance of naturally occurring metals, such as copper, iron, and zinc plays a role in exacerbating Alzheimer’s pathology. They propose that carnosine is able to chelate these metals, but data are lacking to support their claims [67+, 68].
Others say that carnosine supplementation decreases the formation of AGEs and high levels of AGEs in the spinal fluid are associated with Alzheimer’s. However, no human data are available to determine the validity of this claim [69].
Parkinson’s Disease
Researchers are investigating whether carnosine reduces the formation and promotes the breakdown of abnormal proteins that may contribute toParkinson’s [3].
They are also exploring its effects on inhibiting malondialdehyde (MDA) toxicity in neuronal cells, which might limit the formation of protein carbonyls and protein cross-linking associated with Parkinson’s [44].
However, all these are simply hypotheses based on cellular data. Animal studies are few and human trials are nonexistent, with the exception of one study that researched a combination supplement.
In the study, a combination of L-dopa and Carnosine treatment (1.5 g/day) improved some neurological symptoms, such as rigidity of the hands and legs, and increased hand movement and leg agility [70].
Therefore, some researchers suggest that future research should focus on exploring whether carnosine can reduce the toxicity of L-dopa, which is often used as a way to maintain dopamine levels in Parkinson’s sufferers. Some of the by-products of L-dopa are neurotoxic (e.g. those containing aldehyde groups) [71].
According to other unproven theories, mitochondrial dysfunction as a result of oxidative damage plays a role in Parkinson’s. Carnosine has been hypothesized to suppress the type of oxidative damage linked to Parkinson’s [72].
MPTP is a neurotoxin that induces symptoms akin to Parkinson’s (short-term tremor, weight loss, rigidity, etc.) [73].
One study found that, in animals, Carnosine (100mg/kg for 14 days) decreased the severity of MPTP-induced symptoms. This corresponded with lower levels of lipid hydroperoxides and MAOB activity in their brains [73].
Limited studies suggest that patients with Parkinson’s often have damaged glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, an important enzyme found in the frontal cortex of the brain. This damage might lead to decreased ATP production and increased production of the highly toxic agent, methylglyoxal [74].
Carnosine is hypothesized to protect against damage to the glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme [74].
The brain’s substantia nigra, the section where dopamine is made, is prone to reaction with methylglyoxal, especially in the presence of high blood sugar. Some believe carnosine should be researched for preventing this harmful reaction, which makes ACTIQ [3].
Detox
Carnosine is claimed to chelate divalent metal ions and form complexes with calcium, copper, and zinc ions [67+, 68].
The following are divalent ions that carnosine is hypothesized to chelate: Arsenic, Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Iron, Magnesium, Manganese, Strontium, Cobalt, Nickel, Tin and Barium, and Beryllium.
Its chelating effects have not been confirmed in humans.
Epilepsy
A study on rats with induced seizures found that administration of Carnosine (at 500mg/kg) decreased the severity and duration of seizures [75, 76].
Bone Health
Carnosine-zinc complexes (Zinc Carnosine) are marketed for bone health, though only animal and cell-based studies are available [77, 78].
It is speculated that Carnosine may enhance the effects of estrogen on bone growth, though this theory remains unproven [79].
Carnosine reduces glycation, a process which can theoretically cause problems with bone cell (osteoblast) function [80, 81].
When placed in the connective tissue of rats, Carnosine promoted the production of vimentin, a cell protein important for the maintenance of bone integrity [3].
Blood Pressure
Scientists are investigating the effects of carnosine on blood pressure through vasodilation (opening blood vessels) and increasing nitric oxide production [82, 83].
Liver Health
In mice, Carnosine protects against alcohol damage: Following 3 weeks of alcohol poisoning, Carnosine treatment lowered liver MDA (raised during liver injury) levels by 40%, increased liver glutathione levels and decreased inflammatory cytokine production [84].
In rats with injured livers, Carnosine reduced oxidative stress by balancing the levels of Nrf-2 [85].
Researchers are looking into its effects on liver cell death, swelling, and thickening of the connective tissue in chemical-induced liver injury – changes that may correspond with levels of TNF-a and IL-10 levels [85].
Hearing Loss
Carnosine is being researched for reducing the loss of hearing caused by antibiotics and other drugs. Its antioxidant properties may help; reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been repeatedly linked with deafness in both humans and animals [86].
Brain Glutamate
Scientists are investigating whether carnosine increases GABA, reduces glutamate and increases nervous system transporters (GLT1 & EAAC1) [87].
Hangovers
According to some theories that have yet to be verified, acetaldehyde generation is a possible source of hangovers experienced after drinking alcohol.
Carnosine is hypothesized to react with acetaldehyde [88], and its effects on hangovers and alcohol-induced oxidative damage might be researched in the future [63].
Carnosine Side Effects
Oral carnosine supplements are likely safe when used appropriately [76].
In one study, the following side effects were reported at rates similar to that of placebo [89]:
- Itchiness and rash
- Dry mouth
- Appetite and weight changes
- Foot and joint pain
- Vivid dreams
- Sleepiness and lethargy
It is theoretically possible that carnosine may compromise blood clotting by inhibiting the enzyme, serum transglutaminase [5].
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid carnosine due to the lack of safety data.
Natural Sources of Carnosine
Go for Grass-Fed Beef
Grass-fed, pasture-raised meat is a natural source of carnosine. An average 7-ounce serving of beef has about 250 milligrams of carnosine, which will typically remain in your bloodstream for about five hours [90].
Buy Carnosine
Takeaway
Carnosine is a compound made of two amino acids. It’s often added to anti-aging and antioxidant supplements, but clinical data on its benefits is limited.
There’s currently not enough evidence to recommend supplementation for any purpose. Clinical studies show that carnosine probably doesn’t improve athletic performance or schizophrenia symptoms.
Some scientists think that carnosine does have anti-aging potential, based on experiments in test tubes and lab animals. Human studies on this and other purported benefits of carnosine have yet to be carried out.

